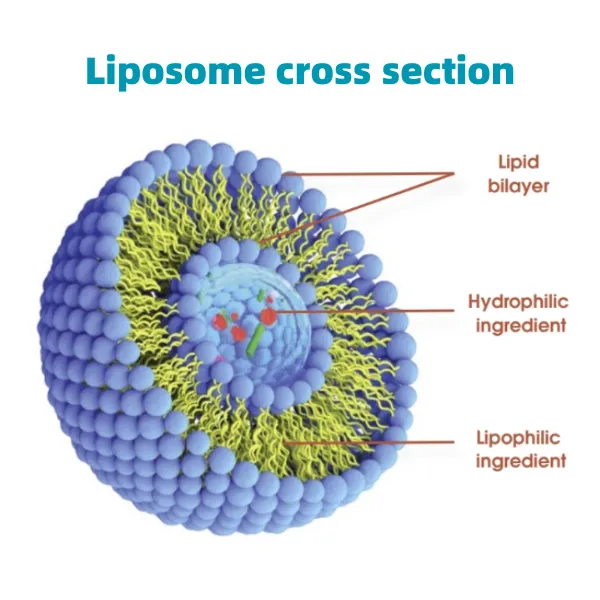
o aminobenzoic acid
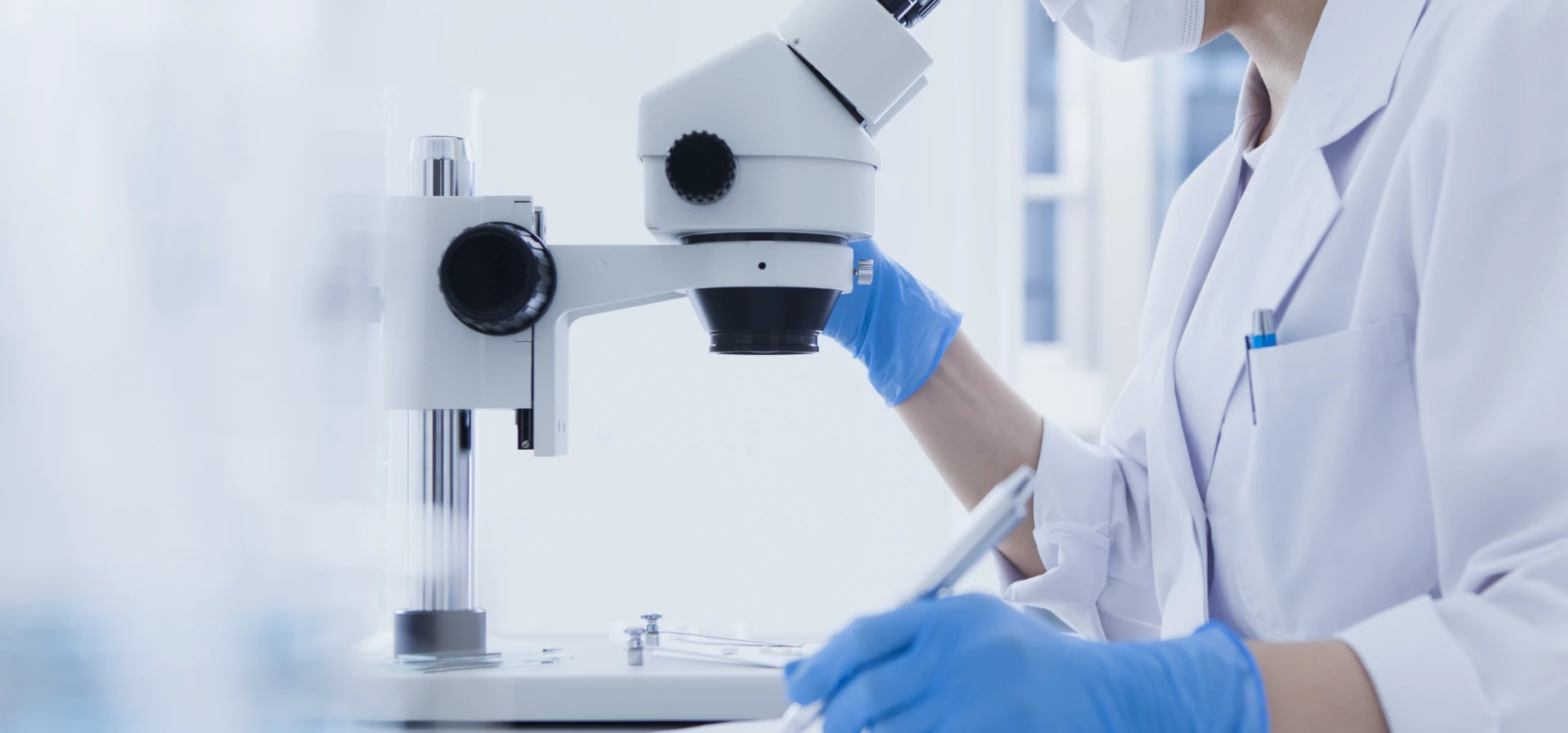
Amino acids are a stable bioavailable complex formed by the coordination bond between essential minerals and amino acids. They break through the absorption limitations of traditional mineral supplements and provide a new way for living organisms to efficiently obtain mineral nutrients. The core characteristic of Amino Acids lies in their unique molecular structure Essential minerals such as calcium, iron, zinc, selenium, etc. form circular structures through chelation reactions with specific amino acids. This structure not only maintains the activity of minerals, but also endows them with protein like biological affinity. Compared to ordinary mineral salts, essential amino acids supplement have stronger molecular stability and can resist damage from factors such as gastric acid and digestive enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract, avoiding precipitation reactions between minerals and other substances and creating favorable conditions for subsequent absorption. In terms of absorption efficiency, Amino Acids exhibit significant advantages Traditional minerals need to undergo complex transformations before they can be absorbed by the intestine, and are susceptible to interference from anti nutritional factors such as phytic acid and oxalic acid, resulting in low absorption rates. And aminos acids can directly enter intestinal cells through the absorption channels of amino acids, bypassing traditional absorption barriers, and the absorption rate can reach 2-3 times that of ordinary minerals. This efficient absorption characteristic can reduce the residual and metabolic burden of minerals in the body, and reduce the side effects caused by excessive supplementation. The application scenarios of Amino Acids are very extensive In the field of nutritional supplementation, amino acid powder can be used as a high-quality raw material for infant formula foods, pregnant women's nutrition supplements, elderly health products, etc., to meet the precise mineral needs of different populations. In animal husbandry, adding such compounds can enhance the absorption and utilization of minerals by livestock and improve growth performance and product quality. In terms of plant cultivation, as a new type of fertilizer additive, it can enhance the crop's ability to absorb minerals, increase yield and nutritional value. In recent years, research on Amino Acids has continued to deepen Researchers further enhance the stability and biological activity of the complex by optimizing the chelation process; Conduct precise research on the combination of specific minerals and amino acids to develop more targeted products. These studies provide theoretical support for its expansion in fields such as healthcare and ecological agriculture. In summary, essential aminos have become important innovative achievements in the field of mineral nutrition due to their stable molecular structure, efficient absorption mechanism, wide application scenarios, and continuous research breakthroughs. It not only solves the problem of low absorption efficiency of traditional mineral supplements, but also provides flexible solutions for nutritional reinforcement in different fields. With the continuous advancement of technology, its value in improving the health level of living organisms and promoting efficient utilization of resources will be further highlighted. Amino Acids FAQs What are Amino Acids and how are they absorbed by the human body? Amino acids are special compounds formed by the combination of amino acids and mineral ions. This type of complex simulates the naturally occurring mineral forms in food, and its unique structure can protect minerals from interference from other components in the digestive tract. During the absorption process, the entire chelate is fully absorbed through the amino acid transport channels of small intestinal epithelial cells. This absorption method significantly improves the bioavailability of minerals, which can be several times higher than the absorption rate of traditional inorganic mineral forms. Why are Amino Acids more effective than regular mineral supplements? Inorganic minerals in traditional mineral supplements can easily combine with phytic acid, oxalic acid, and other substances in the intestine to form insoluble precipitates, leading to absorption obstruction. Amino acids have a stable coordination structure that can resist this interference and ensure the smooth entry of minerals into the bloodstream. Clinical studies have shown that minerals such as iron and zinc in the form of amino acid chelation have a longer retention time in the human body, more precise tissue targeting, and can participate more efficiently in the operation of enzyme systems and physiological functions. Which groups of people are particularly suitable for supplementing with Amino Acids? Elderly people with weak digestive function, patients with intestinal absorption disorders, and pregnant women have a significant demand for such products. Due to the fact that the chelation form of amino acids does not rely on the breakdown of gastric acid, people with insufficient gastric acid secretion can also effectively absorb it. Athletes and postoperative recovered individuals can also benefit from it due to their high mineral demand and high absorption efficiency requirements. For vegetarians, this form of supplementation can compensate for the low bioavailability of minerals in plant-based diets. What are the technical difficulties in the production process of Amino Acids? The preparation of high-quality amino acids requires strict control of chelation rate and molecular weight. The ideal chelating product requires a molar ratio of minerals to amino acids of 1:1-1:3, and a molecular weight of less than 800 daltons to ensure absorption. Directional chelation technology is required during the production process to avoid the formation of ineffective macromolecular polymers. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the amino acid configuration is left-handed, which is more compatible with the structure of human proteins. How to identify high-quality Amino Acid products? High quality products should be clearly labeled with chelation rate indicators, usually above 90% chelation rate to ensure stability. The quality can be preliminarily judged through solubility testing, and true amino acid chelates should maintain a completely dissolved state within the pH range of 3-8. Laboratory testing methods such as infrared spectroscopy can confirm the presence of characteristic coordination bonds, while high-performance liquid chromatography can determine the content of free amino acids. These data can reflect the process level of the product. Consumers can also pay attention to whether there are clinical trials to verify its absorption rate and bioavailability parameters.
Finutra devotes to be an integrated supplier for global supply chain, we offer a
broad array of raw materials and functional ingredients
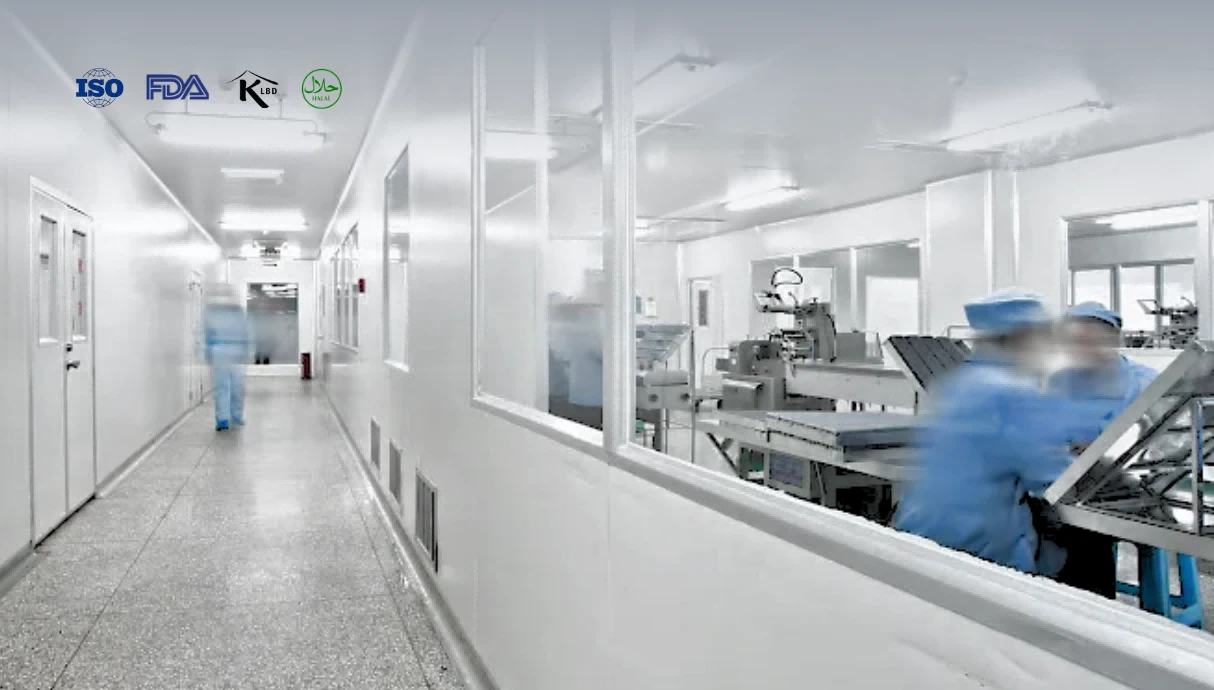
Authoritative Certification
Continuous Innovation, Customer First
Enhance core competitiveness to bring customers better products and services,
Each of these is the result of our team's relentless pursuit of excellence
and our deep commitment to social responsibility.








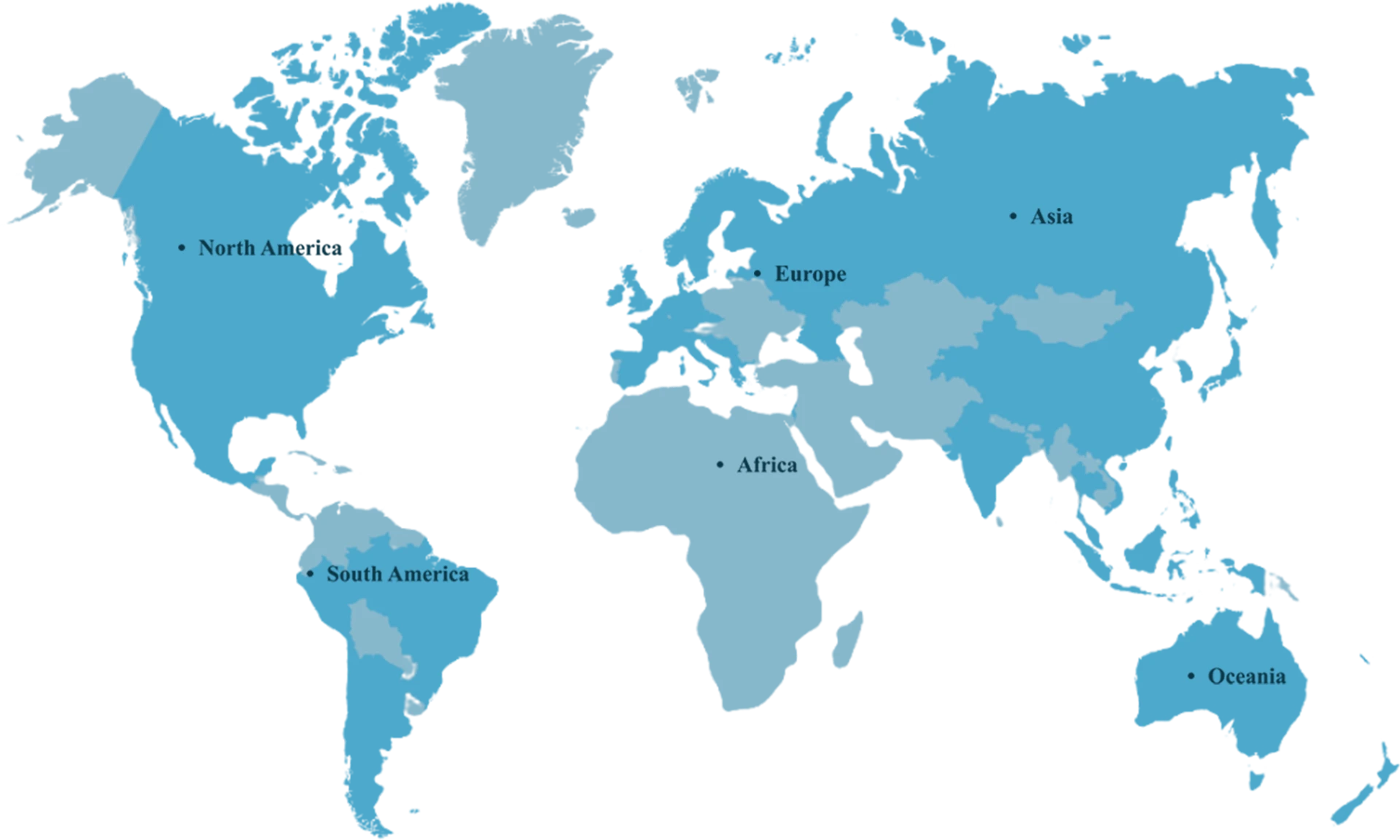
Global
Reach
FINUTRA has over 350,000 square feet of manufacturing and warehouse
space worldwide.
Industries We Serve
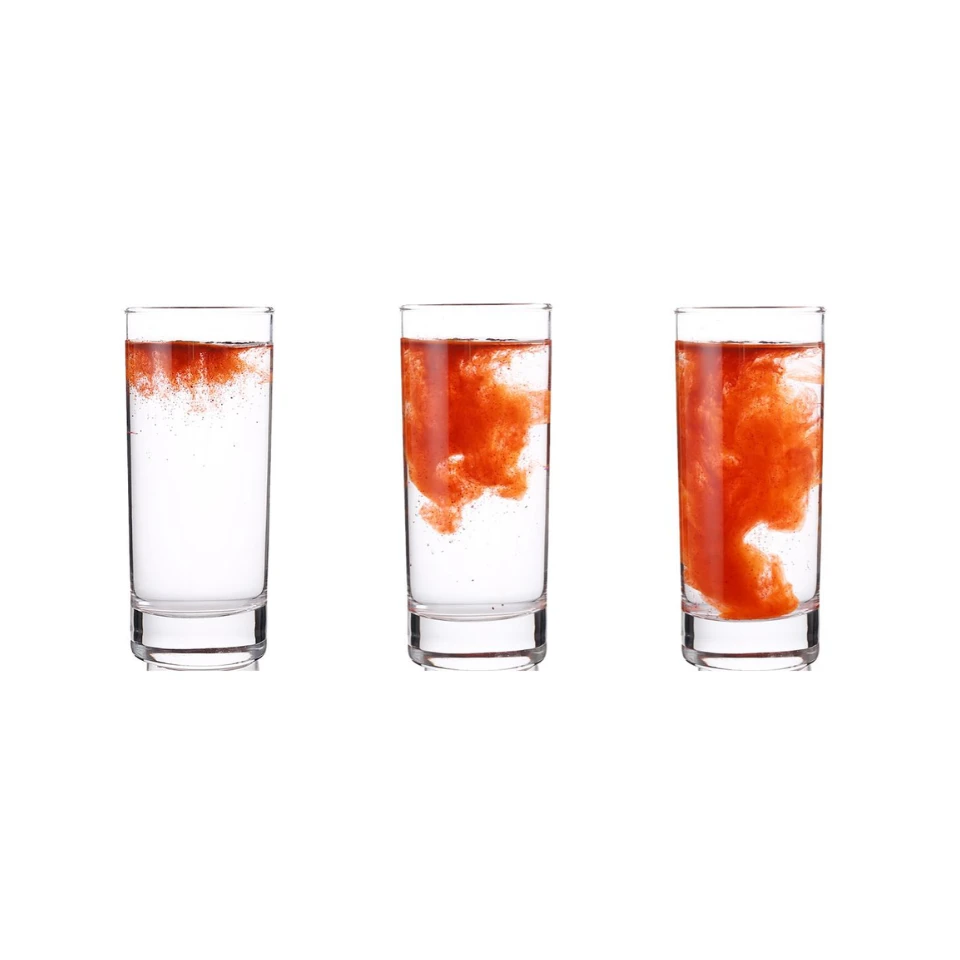
Advanced molecular distillation and microencapsulation
technology. Extremely bioavailable
trace carotenoids Intuitively soluble.


STAY UPDATED
Receive special offers and first look at new
products.
products.
Building 23B1, No.2 Yuanboyuan St., Zhengding Area of China (Hebei) Pilot Free Trade Zone
QUICK LINK
Finutra devotes to be an integrated supplier for global supply chain, we offer a broad array of raw
materials and functional ingredients as a manufacturer, distributor and supplier for global Beverage,
Nutraceutical, Food, Feed and Cosmeceutical.
Copyright © 2025 Hebei Finutra
Biotech Co.,
Ltd. All
Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy